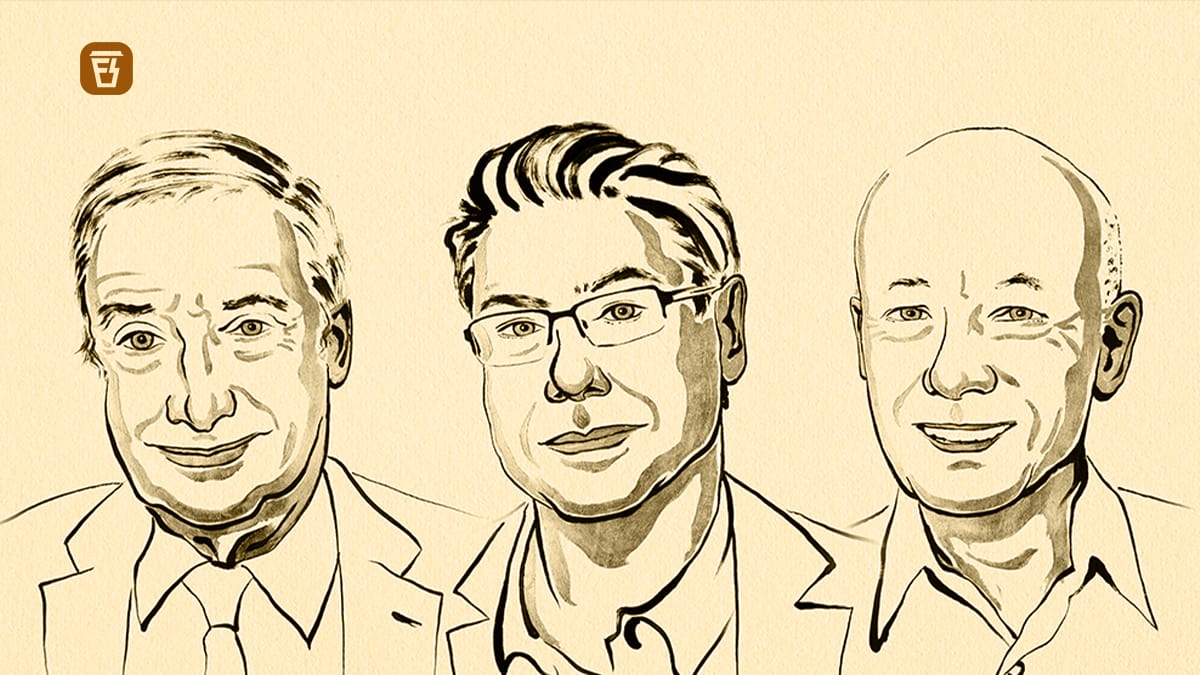
The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences has decided to award the Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel 2025 to Joel Mokyr, Philippe Aghion and Peter Howitt
“for having explained innovation-driven economic growth”
with one half to
1.Joel Mokyr
Affiliations:
Northwestern University (USA) and Tel Aviv University (Israel)Citation:
“For having identified the prerequisites for sustained growth through technological progress.”2.Philippe Aghion
Affiliations: Collège de France and INSEAD (France), London School of Economics (UK)
3.Peter Howitt
Affiliation: Brown University, USA
Joint Citation with Aghion:
“For the theory of sustained growth through creative destruction.”
🧠 Theme of the Prize (2025):
“For having explained innovation-driven economic growth.”
🌍 Background: Why This Matters
For most of human history, economies were stagnant — living standards barely improved over centuries.
The Industrial Revolution (18th–19th centuries) changed this pattern — ushering in sustained economic growth driven by technological progress.
The 2025 laureates explain why and how innovation became self-sustaining, enabling long-term prosperity.
📘 Key Contributions
1. Joel Mokyr: The Historical Roots of Innovation-Driven Growth
Focus: Historical and cultural foundations of sustained technological progress.
Approach: Used historical evidence and economic reasoning to understand how innovation became continuous.
🔹 Major Insights:
Before the Industrial Revolution:
Innovation was sporadic — occasional inventions didn’t lead to continuous progress.
Reason: People knew what worked but not why — there was little scientific understanding.
After the Industrial Revolution:
Scientific thinking and experimentation merged — leading to systematic innovation.
Knowledge became cumulative (each discovery built on previous ones).
Societies became open to new ideas, tolerating experimentation and risk.
This cultural openness and curiosity created a self-reinforcing cycle of innovation.
📎 UPSC Angle:
Link to GS Paper 1 (World History): Industrial Revolution.
Link to GS Paper 3 (Economy): Innovation, Research & Development, Economic Growth.
Takeaway: Knowledge, openness, and institutional support are prerequisites for sustained economic growth.
2. Philippe Aghion & Peter Howitt: The Theory of Creative Destruction
Origin: Their landmark paper (1992) formalized the idea of “creative destruction.”
Concept borrowed from: Joseph Schumpeter (1942), who first coined the term.
🔹 What Is Creative Destruction?
When new technology or products replace old ones, driving economic progress.
Example:
Smartphones replaced feature phones.
Renewable energy is replacing coal-based power.
🔹 Key Elements of Their Model:
Innovation is both creative and destructive:
Creative → New products, methods, and efficiency.
Destructive → Old firms and technologies become obsolete.
Growth is sustained only if innovation continues.
Competition and incentives drive innovation — entrepreneurs innovate for profit.
Institutions and policies must manage the social conflicts arising from this process.
🔹 Managing the Conflicts:
Creative destruction creates winners and losers:
New firms and innovators gain.
Old firms and workers in obsolete industries lose.
If incumbents (big firms, interest groups) block innovation to protect themselves, growth slows.
Therefore, policy must protect competition and ensure social safety nets for displaced workers.
📎 UPSC Angle:
GS Paper 3:
Inclusive Growth
Industrial Policy
Innovation Ecosystem
Role of Competition in Markets
Essay Topics:
“Innovation as the Engine of Growth”
“Balancing Growth and Equity in the Age of Technology”
⚖️ Overall Message of the 2025 Nobel
“Economic growth cannot be taken for granted. We must uphold the mechanisms that sustain innovation and creative destruction.”
Key Mechanisms to Sustain Growth:
Open societies and institutions that encourage new ideas.
Scientific reasoning and education that deepen understanding.
Free competition to prevent monopolies from blocking innovation.
Policy frameworks that:
Encourage R&D and startups.
Provide safety nets and skill retraining for displaced workers.
Ensure equitable growth while maintaining dynamism.
📈 Relevance for UPSC (Prelims + Mains)
| Paper | Relevance |
|---|---|
| Prelims | Current Affairs: Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences 2025 |
| GS Paper 1 | Industrial Revolution, Economic History |
| GS Paper 3 | Economic Growth, Innovation, Technology, Inclusive Development |
| Essay Paper | Topics on Growth, Innovation, Technology, Inequality |
| Interview | Application-based questions on innovation and economic policy |
💬 Possible UPSC Mains Questions
“Discuss the concept of ‘creative destruction’ and its role in sustaining economic growth.”
“According to Joel Mokyr, cultural openness and scientific thinking were key to sustained growth. Explain.”
“How can India balance innovation-driven growth with social equity?”
“Explain the role of knowledge and institutions in driving long-term economic growth.”
🌐 Contemporary Relevance for India
Startup India and Digital India reflect the push toward innovation-driven growth.
Creative destruction evident in:
E-commerce replacing traditional retail.
Electric vehicles replacing fossil-fuel-based mobility.
Fintech replacing traditional banking models.
Policy challenge: Managing transition without social disruption.
📚 Key Takeaways Summary
| Concept | Key Idea |
|---|---|
| Joel Mokyr | Historical roots: Knowledge, culture, and openness drive sustained innovation. |
| Aghion & Howitt | Theoretical model: Growth through creative destruction. |
| Core Lesson | Innovation sustains growth; resistance to change leads to stagnation. |
| Policy Implication | Promote competition, R&D, education, and social inclusion. |
🔗 For Further Reading
Schumpeter, “Capitalism, Socialism and Democracy” (1942)
Aghion & Howitt, “A Model of Growth through Creative Destruction” (1992)
Joel Mokyr, “The Gifts of Athena” (2002)
✅ In Essence:
Innovation is the engine of growth, but growth is sustainable only when societies embrace change, support creativity, and manage the disruptions it causes.
For more such UPSC-focused current affairs analysis, visit www.victorgrowth.com 🚀