1. Recent Development
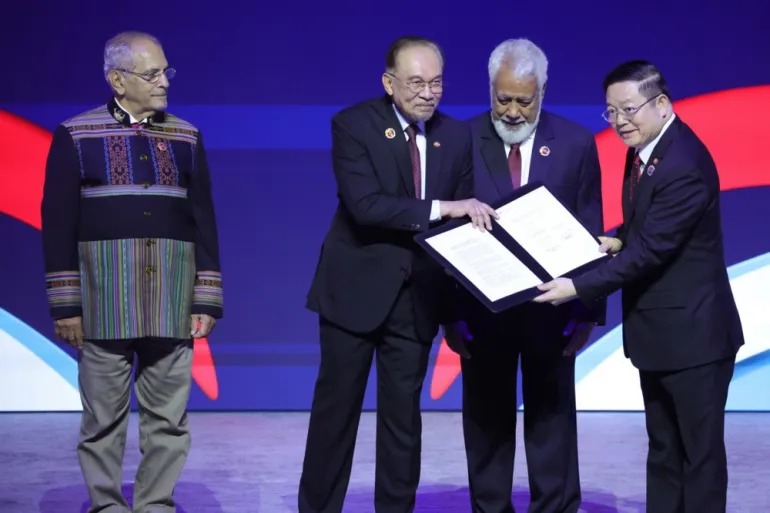
East Timor (Timor-Leste) has officially become the 11th member of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN).
The announcement was formalised during the ASEAN Summit in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia (October 2025).
The event was marked by the ceremonial raising of East Timor’s national flag alongside those of other ASEAN nations — symbolising its full inclusion in the regional bloc.
2. Background and Journey to Membership
(a) Application and Wait
East Timor first applied for ASEAN membership in 2011.
It waited 14 years before full admission in 2025, after gaining observer status in 2022.
The membership marks the culmination of nearly five decades of aspiration and diplomacy since the nation’s independence struggle began.
(b) Historical Significance
The accession reflects ASEAN’s principle of inclusivity and regional unity, extending membership to all countries in Southeast Asia.
For East Timor, it represents recognition of its sovereignty and democratic progress on the international stage.
3. Political Leadership and Symbolism
President: José Ramos-Horta — a Nobel Peace Prize laureate (1996) for efforts in resolving East Timor’s conflict peacefully.
Prime Minister: Xanana Gusmão — a freedom fighter and independence hero.
Both leaders see ASEAN membership as the fulfilment of a long-standing national dream and a gateway to economic and political stability.
4. Economic and Developmental Context
(a) Economic Status
GDP: Around USD 2 billion (one of Asia’s smallest economies).
Population: Approximately 1.4 million people.
In contrast, ASEAN’s total GDP is about USD 3.8 trillion, highlighting the vast economic gap.
(b) Expected Benefits
ASEAN membership offers East Timor:
Access to regional trade networks and investment opportunities.
Integration into ASEAN’s economic initiatives such as digital transformation and sustainable development programs.
Boost to infrastructure, education, and energy sectors through regional cooperation and foreign investment.
A platform to diversify its economy beyond oil and gas dependence.
(c) Strategic Goals
Prime Minister Gusmão termed it as a “new chapter of immense opportunities” — focusing on trade, connectivity, and human development.
The country hopes to align its policies with the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) framework for inclusive growth.
5. Historical and Political Background
(a) Colonial Legacy and Independence
East Timor was a Portuguese colony for over 400 years.
Declared independence in 1975, but was invaded by Indonesia shortly after.
Under Indonesian occupation (1975–1999), it faced major humanitarian and political crises.
Following a UN-administered referendum in 1999, East Timor voted overwhelmingly for independence.
Achieved full sovereignty in 2002, becoming the first new nation of the 21st century.
(b) Democratic Transition
Post-independence, East Timor has evolved as a democratic and peaceful nation, maintaining strong ties with both ASEAN and the UN.
6. Strategic and Geopolitical Significance
(a) For ASEAN
East Timor’s inclusion completes ASEAN’s geographical coverage of mainland and maritime Southeast Asia.
Strengthens ASEAN’s image as an inclusive, cohesive regional organisation.
Adds to the bloc’s peacebuilding and conflict-resolution experience, given East Timor’s history of struggle and reconciliation.
(b) For East Timor
Enhances its regional legitimacy and foreign policy standing.
Provides security assurances through ASEAN’s political and security frameworks.
Opens doors for capacity-building and regional partnership programs.
(c) Broader Context
Comes at a time of rising geopolitical competition in Southeast Asia, particularly concerning the South China Sea disputes and major power rivalry (U.S.–China–Russia).
East Timor’s participation strengthens ASEAN’s collective voice in regional diplomacy.
7. Future Role within ASEAN
Expected to contribute actively in:
Peacebuilding and mediation efforts, drawing from its own reconciliation experience.
Sustainable development, particularly in small island and least developed country (LDC) contexts.
Regional stability initiatives, including dialogues on the South China Sea and climate resilience.
President Ramos-Horta emphasised that East Timor would be a “bridge of peace and cooperation” within ASEAN.
About ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations)
Establishment:
Formed in 1967 in Bangkok (Thailand) with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration).
Headquarters:
Jakarta, Indonesia.
Objective:
To promote economic growth, political stability, social progress, and regional peace and security among member states.
Strengthen cultural ties and mutual cooperation in Southeast Asia.
Members (10 countries):
Brunei Darussalam
Cambodia
Indonesia
Laos
Malaysia
Myanmar
Philippines
Singapore
Thailand
Vietnam
India’s Status:
India is not a member of ASEAN.
However, India is an important dialogue partner and a key player in ASEAN-led regional forums such as:
East Asia Summit (EAS)
ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF)
ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting Plus (ADMM+)
Economic and Strategic Importance
Trade and Economy:
ASEAN is one of India’s largest trading partners.
Accounts for about 11% of India’s total global trade.
Key sectors: electronics, machinery, petroleum products, textiles, and services.
Connectivity and Cooperation:
India’s “Act East Policy” gives special focus to strengthening ties with ASEAN countries.
Cooperation areas include maritime security, digital economy, infrastructure, climate change, and counter-terrorism.
Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP):
ASEAN led the creation of the RCEP, the world’s largest free trade agreement.
Members include ASEAN + 5 (China, Japan, South Korea, Australia, New Zealand).
India opted out of RCEP in 2019, citing concerns over trade imbalances and domestic industry protection.
8. Exam-Oriented Facts Summary
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Country Name | East Timor / Timor-Leste |
| Capital | Dili |
| Independence | 2002 (from Indonesia, post-UN referendum) |
| Applied for ASEAN Membership | 2011 |
| Observer Status | 2022 |
| Full ASEAN Membership | October 2025 |
| ASEAN Member Count | Now 11 members |
| President | José Ramos-Horta (Nobel Peace Prize, 1996) |
| Prime Minister | Xanana Gusmão |
| GDP | ~USD 2 billion |
| Population | ~1.4 million |
| Host of Accession Summit | Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia |
| Significance | Enhances ASEAN unity and inclusiveness |
9. Relevance for UPSC
(a) GS Paper II – International Relations
ASEAN structure and evolution (founded in 1967).
India–ASEAN relations and regional diplomacy.
Importance of inclusivity and cooperation in regional organisations.
(b) GS Paper I – Post-Independence World
Decolonization and emergence of new nations (example: East Timor, 2002).
(c) GS Paper III – Economy
Economic integration and development of small economies through regional blocs.
10. Conclusion
East Timor’s accession to ASEAN marks a historic milestone for both the nation and the regional bloc.
It symbolizes unity, inclusivity, and the success of diplomacy over decades of struggle.
For ASEAN, it reinforces its identity as a comprehensive, people-oriented, and community-driven regional organization; for East Timor, it opens a path toward stability, development, and international partnership.