Indian Army
🔹 What It Is
The Technical Entry Scheme (TES) is a direct recruitment route into the Indian Army for students who have completed Class 12 with Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics (PCM). It is designed for young aspirants who wish to pursue an engineering career in the Armed Forces and serve as commissioned technical officers.
Similar technical-entry options also exist in the Indian Navy and Air Force.
🔹 Eligibility
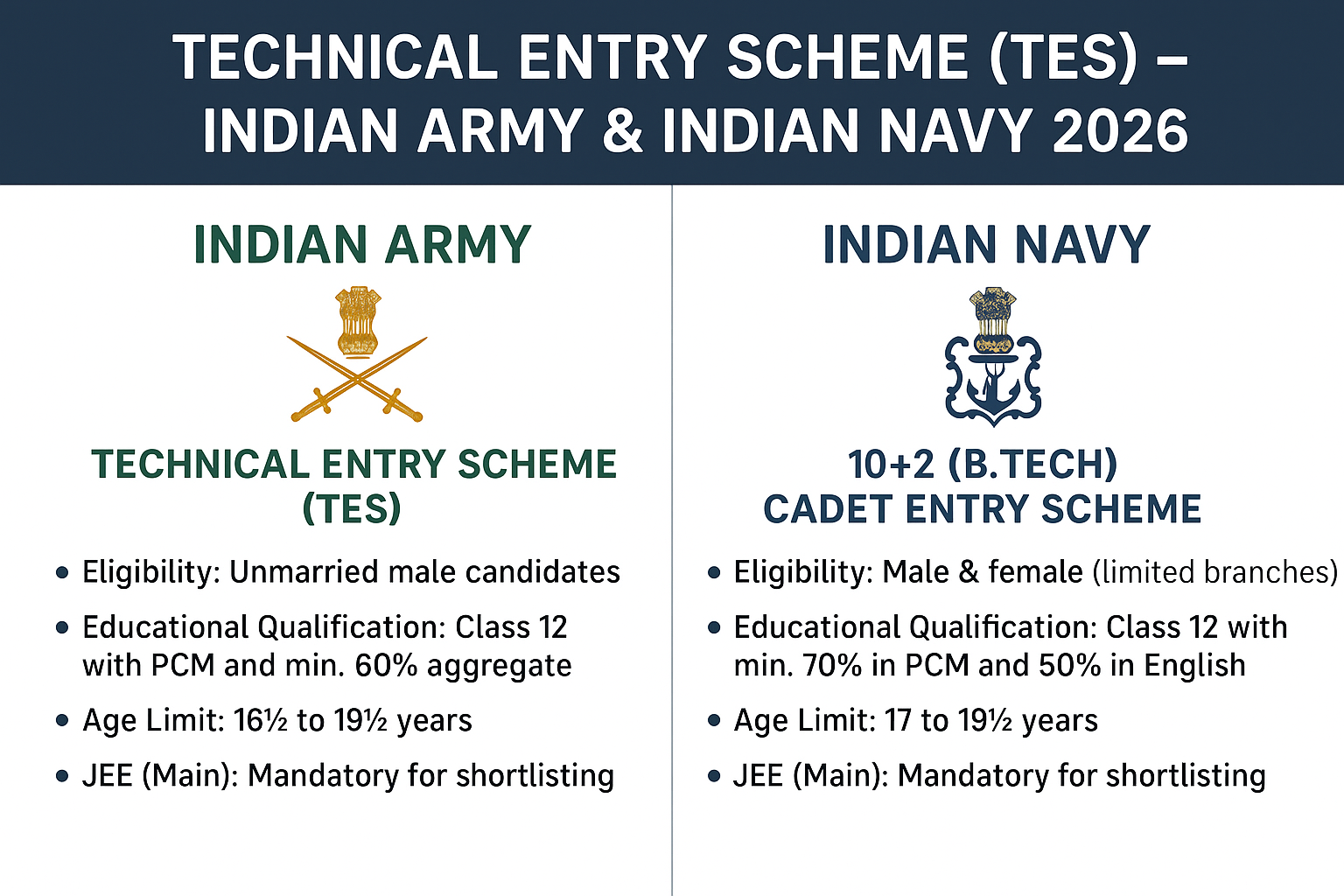
Gender: Unmarried Male Candidates
Educational Qualification: Class 12 (10+2) with PCM and minimum 60% aggregate
Age Limit: 16½ to 19½ years
JEE (Main): Mandatory for shortlisting
🔹 Selection Process
Shortlisting of candidates based on Class 12 marks and JEE (Main) score
SSB Interview for shortlisted candidates
Medical Examination
Final Merit List based on overall performance
There is no separate written exam like in the NDA. Selection is purely on academic and interview merit.
🔹 Advantages
✅ Direct entry after Class 12 without UPSC written exam
✅ Ideal for students with strong technical and engineering aptitude
✅ Provides an opportunity to serve as an officer in the Indian Army’s technical corps
✅ Candidates earn an Engineering degree during training
🔹 Disadvantages
❌ Limited only to technical branches of the Army
❌ Requires strong PCM and JEE performance
❌ Restricted to male candidates only
❌ Narrow eligibility window (16½–19½ years)
⚓ 10+2 (B.Tech) Cadet Entry Scheme – Indian Navy
🔹 What It Is
The 10+2 (B.Tech) Cadet Entry Scheme is a premier recruitment path into the Indian Navy for students who have completed Class 12 with PCM.
Selected candidates undergo four years of B.Tech training at the Indian Naval Academy (INA), Ezhimala and are commissioned as officers upon successful completion.
This scheme offers both academic and military training simultaneously.
🔹 Eligibility
Gender: Male & Female (limited branches)
Educational Qualification: Class 12 (10+2) with minimum 70% in PCM and 50% in English (10th or 12th)
JEE (Main): Mandatory for shortlisting
Age Limit: 17 to 19½ years
🔹 Selection Process
Application & shortlisting based on JEE (Main) score
SSB Interview for shortlisted candidates
Medical Examination
Final Merit List & Training at INA
Completion of 4-year B.Tech program leading to commissioning as a Sub-Lieutenant
🔹 Advantages
✅ Provides a B.Tech degree + officer training
✅ Open to both male and female candidates
✅ Direct entry without written exam
✅ Opportunity to serve as a commissioned officer in the Executive or Technical branches of the Indian Navy
🔹 Disadvantages
❌ Requires very high academic and JEE performance
❌ Only open to PCM students
❌ Focused mainly on technical and engineering roles
❌ Limited number of seats and branches for female candidates
⚖️ Summary
| Feature | Army TES (10+2) | Navy 10+2 (B.Tech) Entry |
|---|---|---|
| Service | Indian Army | Indian Navy |
| Educational Requirement | 10+2 with PCM (60%) | 10+2 with PCM (70%) + English 50% |
| JEE (Main) | Mandatory | Mandatory |
| Gender | Male Only | Male & Female |
| Age Limit | 16½ – 19½ years | 17 – 19½ years |
| Degree Awarded | Engineering (Army-affiliated) | B.Tech (JNU-affiliated at INA) |
| Training Academy | OTA Gaya + CME/MCTE/MCEME | Indian Naval Academy (Ezhimala) |
| Commission Rank | Lieutenant | Sub-Lieutenant |
| Written Exam | No | No |
🎯 In Short
Both TES (Army) and 10+2 (B.Tech) Entry (Navy) offer excellent opportunities for science stream students right after Class 12 to become commissioned officers.
TES is best suited for male students aiming for the Army’s technical branches.
The Navy 10+2 (B.Tech) scheme is ideal for both male and female aspirants with strong PCM and JEE scores who want an engineering + officer career in the Indian Navy.