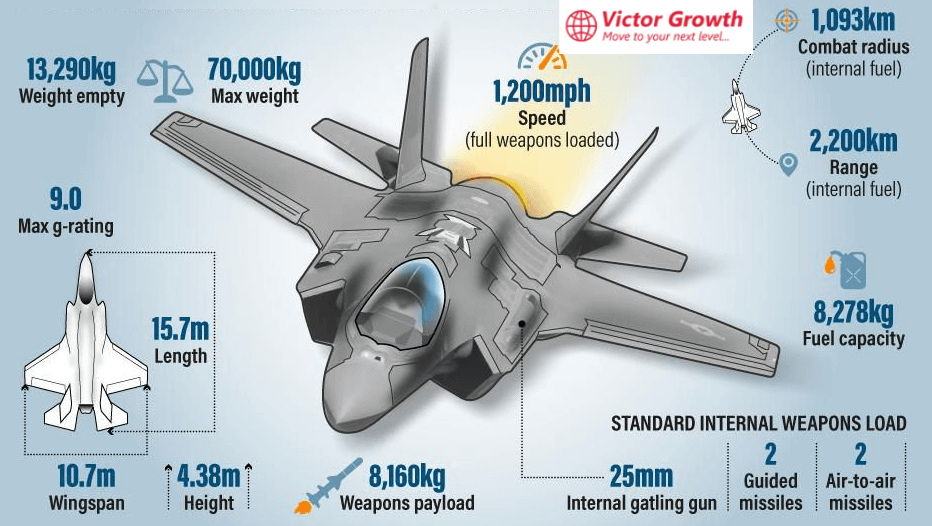
F-35 vs Rafale: A Complete Comparison for India’s Defense
India’s potential acquisition of the Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II has sparked significant debate in defense circles. While the Dassault Rafale, already in service with the Indian Air Force (IAF), is a formidable fighter, the F-35 is a next-generation stealth aircraft with unique advantages. This article explores the special features of the F-35 and compares it with the Rafale, analyzing their capabilities, strengths, and limitations.
Special Features of the F-35 Lightning II
The Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II is a fifth-generation multirole stealth fighter designed for air superiority, ground attack, and electronic warfare. Here are its standout features:
1. Stealth & Low Observable Technology
- The F-35 has an advanced stealth design, making it nearly invisible to enemy radar.
- Radar-absorbing materials and an optimized airframe reduce its radar cross-section (RCS).
- Rafale: While Rafale has some stealth features (reduced radar signature), it is not a full-stealth aircraft.
2. Sensor Fusion & Avionics
- The F-35 integrates data from multiple sensors into a single real-time display for better situational awareness.
- The Distributed Aperture System (DAS) provides 360-degree coverage for missile detection and tracking.
- Rafale: While Rafale has excellent avionics with the RBE2 AESA radar, it does not have the same level of networked sensor fusion as the F-35.
3. Advanced Radar & Electronic Warfare (EW)
- The AN/APG-81 AESA radar is one of the most powerful fighter radars, allowing deep penetration attacks without detection.
- The AN/ASQ-239 Barracuda EW system provides electronic attack, jamming, and defensive countermeasures.
- Rafale: The Rafale’s Spectra EW suite is highly advanced but does not offer the same level of automation and AI-driven jamming as the F-35.
4. Data Link & Network Warfare
- The F-35 acts as a data hub, linking multiple assets (AWACS, drones, ships) in real time.
- Its MADL (Multifunction Advanced Data Link) provides encrypted communication for seamless coordination.
- Rafale: Uses the Link 16 data link, which is effective but not as futuristic as the MADL on the F-35.
5. Weapons & Combat Capabilities
- The F-35 carries a mix of air-to-air, air-to-ground, and anti-ship weapons, including:
- AIM-120 AMRAAM (Beyond Visual Range missile)
- AIM-9X Sidewinder (Short-range missile)
- StormBreaker Smart Bombs
- JASSM-ER (Long-range cruise missile)
- B61 Nuclear Bombs (for nuclear strike capability)
- Rafale: Equipped with:
- Meteor (BVRAAM) – Superior range over AMRAAM
- MICA, SCALP, and Hammer Missiles
- Exocet Anti-Ship Missiles
- ASMP-A Nuclear Missile (French version only)
6. Short Takeoff & Vertical Landing (STOVL)
- The F-35B variant has vertical landing capability, useful for aircraft carriers with small decks.
- Rafale: Cannot perform vertical takeoff or landing.
7. AI & Automation
- The F-35 uses AI-driven decision-making, reducing pilot workload.
- The Helmet-Mounted Display System (HMDS) replaces traditional cockpit instruments, displaying all critical data inside the helmet.
- Rafale: Uses a Head-Up Display (HUD) and Helmet-Mounted Sight, but lacks the full AI-driven automation of the F-35.
8. Maintenance & Logistics
- The F-35 uses the Autonomic Logistics Information System (ALIS) for predictive maintenance.
- Rafale: Requires manual maintenance planning but is known for reliability and easy servicing.
F-35 vs Rafale: A Head-to-Head Comparison
| Feature | F-35 Lightning II | Dassault Rafale |
|---|---|---|
| Generation | 5th Generation | 4.5 Generation |
| Stealth | Full Stealth (Low Observable) | Partial Stealth (Reduced RCS) |
| Radar | AN/APG-81 AESA | RBE2 AESA |
| Avionics | AI-driven, Integrated Sensor Fusion | Advanced but lacks full AI integration |
| Weapons | AMRAAM, Sidewinder, StormBreaker, JASSM-ER | Meteor, MICA, SCALP, Exocet |
| Electronic Warfare | Barracuda EW Suite | Spectra EW Suite |
| Combat Radius | ~1,380 km | ~1,850 km |
| Speed | Mach 1.6 | Mach 1.8 |
| Thrust Vectoring | No | No |
| Takeoff & Landing | STOVL (F-35B) | Conventional |
| Data Link | MADL (Better network warfare) | Link 16 |
| Maintenance | AI-based predictive maintenance | Manual maintenance |
Should India Buy the F-35?
While the Rafale is a battle-proven, highly agile 4.5-generation fighter, the F-35 is a next-gen stealth aircraft with advanced electronic warfare and AI capabilities. However, several challenges exist:
- Cost: The F-35 costs $80–100 million per unit, while Rafale costs around $85 million. The maintenance of the F-35 is significantly higher.
- Compatibility: India’s fleet includes Sukhoi Su-30MKI, Tejas, Mirage 2000, and Rafale. Integrating the F-35 into an existing mix of Russian and Western systems may be difficult.
- Geopolitical Concerns: India’s purchase of the Russian S-400 air defense system has previously led to U.S. sanctions threats. Would buying the F-35 create diplomatic friction?
- Mission Requirements: The Rafale is better for high-speed air dominance and deep strikes, whereas the F-35 is optimized for stealth penetration and electronic warfare.
Best Option for India?
- If India wants stealth and future-ready network warfare, the F-35 is the best choice.
- If India prefers an agile, combat-proven, cost-effective solution, the Rafale remains a better option.
Conclusion
The decision to buy the F-35 would be a game-changer for India’s defense, marking a strategic shift toward the U.S. However, it comes with challenges related to cost, integration, and geopolitical risks. The Rafale, with its superior agility and battle-proven reliability, remains the best choice for immediate threats.
India must carefully weigh operational needs, budget, and long-term strategy before making a final decision.