🔹 Definition
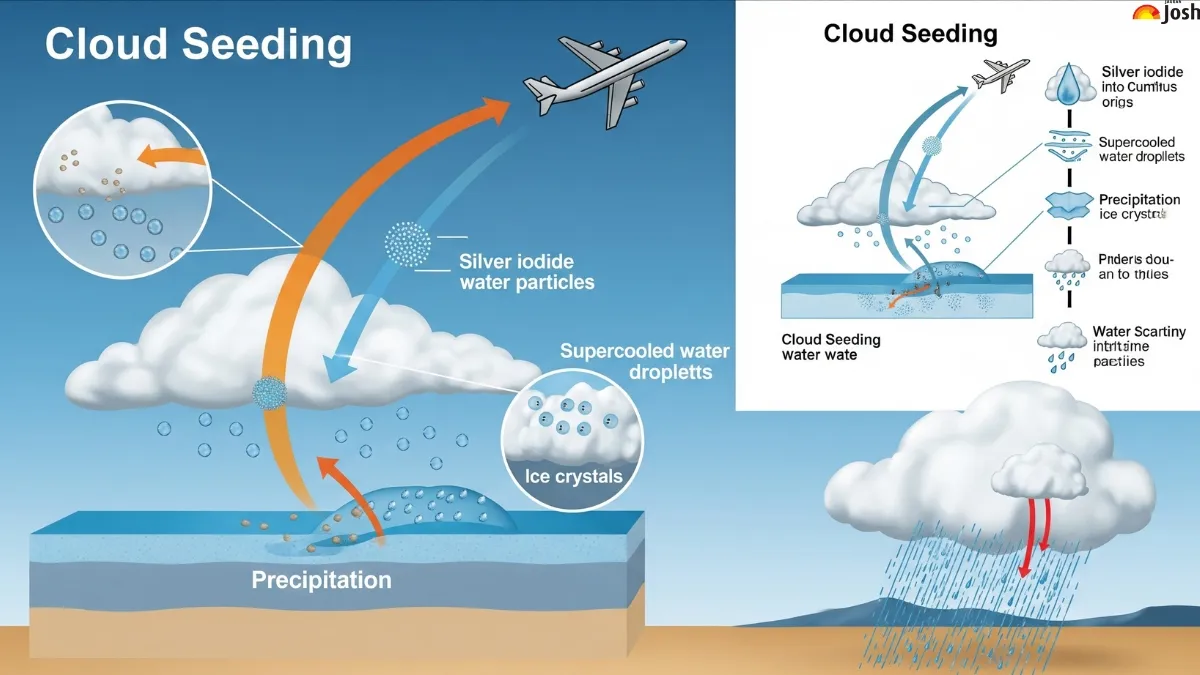
Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique that artificially induces rainfall by dispersing certain chemical substances into clouds to encourage condensation of water vapour into raindrops.
☁️ Scientific Principle
Works on the principle that water vapour condenses onto particles called Cloud Condensation Nuclei (CCN).
The seeding agents act as nuclei around which moisture condenses to form droplets, eventually leading to precipitation.
🔸 Common Seeding Agents
Silver iodide (AgI)
Potassium iodide (KI)
Dry ice (solid CO₂)
Liquid propane
Calcium chloride (CaCl₂) — used in some Indian experiments (e.g., Solapur).
☁️ Conditions Required for Effective Cloud Seeding
Pre-existing Clouds: Seeding cannot create clouds — it only enhances rainfall from existing ones.
Tall, Moist Clouds: More vertical development increases seeding effectiveness.
Low Wind Conditions: Prevents dispersal of seeding material before it acts.
Appropriate Humidity and Temperature: Ensures condensation and droplet formation.
⚙️ Different Cloud Seeding Methods
| Type | Technique | Key Feature | Example/Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Hygroscopic Cloud Seeding | Salts like NaCl or CaCl₂ are sprayed using explosives into the lower portions of warm clouds. | Promotes condensation by providing large nuclei. | Used in Solapur experiment, Maharashtra. |
| 2. Static Cloud Seeding | Chemicals like silver iodide crystals are dispersed into cold clouds. | Induces ice crystal formation that grows and falls as rain/snow. | Common in hill regions. |
| 3. Dynamic Cloud Seeding | Aims to strengthen vertical air currents to enhance moisture uplift. | Leads to formation of more droplets → more rainfall. | Used in large-scale experiments in the USA, China. |
🌧️ Applications of Cloud Seeding
1. Increasing Rainfall
Used in drought-prone regions to augment natural rainfall.
Supports agriculture and water security.
2. Geoengineering & Climate Research
Studied as a climate engineering tool to counter regional droughts or mitigate local warming.
3. Weather Regulation
Suppresses hail, disperses fog, and can modify cyclone intensity.
4. Pollution Control
Artificial rain helps wash out pollutants and reduce particulate matter (PM2.5 & PM10) concentrations in the air.
5. Aviation Applications
Used to disperse supercooled fog near airports to improve visibility and ensure flight safety.
⚠️ Limitations of Cloud Seeding
❌ Not a Drought Solution: Can only supplement, not replace, long-term water resource management.
☁️ Cloud Dependency: Cannot work without moisture-bearing clouds.
💧 Environmental Concerns: Silver iodide and other chemicals may contaminate water and soil.
🌍 Weather Imbalance: Excessive rainfall in unintended areas may cause flash floods or soil erosion.
🧪 Health Impact: Toxic compounds (like AgI) can harm ecosystems and human health.
🌡️ Potential Climate Effects: Some agents may contribute to greenhouse gas accumulation.
🇮🇳 Cloud Seeding Experiments in India
Karnataka: Seeding done under “Varshadhare Project” for drought relief.
Maharashtra: Solapur experiment using hygroscopic seeding (CaCl₂ flares).
Tamil Nadu & Andhra Pradesh: Experiments during weak monsoon years.
Delhi (Proposed): To mitigate severe winter air pollution through artificial rainfall.
🏙️ Delhi Air Pollution: A Context for Cloud Seeding
🔸 Current Status
Delhi experiences hazardous air quality every winter.
In early 2025, it was ranked India’s 2nd most polluted city (Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air – CREA).
🌫️ Major Causes of Delhi’s Air Pollution
🚗 Vehicle Emissions
Accounts for ~40% of winter PM2.5 levels.
High diesel vehicle usage worsens emissions.
🏭 Industrial Emissions
NCR industries emit SO₂, NOx, and PM2.5, particularly from power plants and manufacturing units.
🏗️ Construction and Demolition Dust
Major source of PM10; poor dust control mechanisms increase coarse particulate matter.
🔥 Waste Burning
Open burning of garbage and plastic adds toxic pollutants.
🌾 Stubble Burning
Crop residue fires in Punjab, Haryana, and Western UP elevate pollution levels each autumn.
🌬️ Weather Inversion (Winter Inversions)
A layer of warm air traps cooler air near the ground.
Pollutants remain suspended close to the surface, worsening smog conditions.
🌧️ Why Cloud Seeding is Considered in Delhi
To artificially induce rain and wash pollutants (especially PM2.5 and PM10) from the atmosphere.
Acts as an emergency short-term measure to improve air quality during severe pollution episodes.
Previous attempts (2018, 2023 proposals) faced technical and meteorological limitations due to lack of suitable cloud conditions.
🔍 Significance for UPSC
🧭 Prelims Relevance
Concept of weather modification and cloud seeding agents.
Basics of particulate matter and air inversion phenomena.
🧭 Mains Relevance (GS Paper 3)
Environment & Pollution: Innovative technologies for pollution control.
Disaster Management: Addressing drought and extreme weather.
Science & Tech: Application of atmospheric sciences.
💡 Way Forward
Scientific Validation: Need long-term, evidence-based studies on effectiveness.
Environmental Safety: Use eco-friendly seeding agents.
Integrated Approach: Combine with emission reduction policies and green energy adoption.
Weather Forecasting Infrastructure: Improve cloud monitoring through Doppler radars and satellite data.
Public Awareness: Clarify that cloud seeding is a temporary supplement, not a permanent solution.
✅ In Summary
Cloud seeding is a scientifically innovative but limited tool for rainfall enhancement and pollution mitigation.
While it holds potential for short-term relief, sustainable pollution control in Delhi requires structural reforms in transport, energy, agriculture, and waste management.