1. What is the GFP Index?
The Global Firepower (GFP) Index is an annual ranking that assesses the conventional war-fighting potential of 145 countries using 60+ quantitative and qualitative factors (manpower, equipment, defence budgets, logistics, geography, industry, etc.). Global Firepower
2. How GFP measures military strength (methodology — concise)
Power Index (PwrIndx): GFP combines many indicators into a single numeric Power Index (lower = stronger). Global Firepower
Major factor groups: manpower (active + reserves), land forces (tanks, artillery), airpower (aircraft, AWACS), naval assets (submarines, carriers), defence spending, logistics & industry (production, stockpiles), geography, and certain qualitative measures (training, force readiness). Global Firepower
Usefulness: good for comparative, high-level snapshots of conventional capabilities.
Caveat: GFP does not measure combat experience, leadership, doctrine, nuclear posture (only counts as a factor), political will, alliances, or qualitative edge in every dimension.
3. 2025 — Top 4 (short summary)
United States — Rank 1. PwrIndx ~0.0744; unmatched global reach across land, sea, air, space and cyber; largest technological edge and logistics network. Global Firepower+1
Russia — Rank 2. Massive armour/artillery and large nuclear arsenal; continues modernization (air-defence, missiles). Global Firepower
China — Rank 3 (tied with Russia in power index value area). Rapid modernization, biggest standing force, expanding blue-water navy, strong missile and cyber focus. Global Firepower+1
India — Rank 4. Large manpower, rising defence budget, growing indigenization (Atmanirbhar Bharat) and modernisation of key platforms. Global Firepower
4. Country-wise pointwise details (for answers/notes)
United States (Rank 1)
Why ranked #1: global force projection (carrier strike groups, expeditionary logistics), technological superiority (stealth fighters, long-range precision, space & ISR), large defence industrial base. Global Firepower
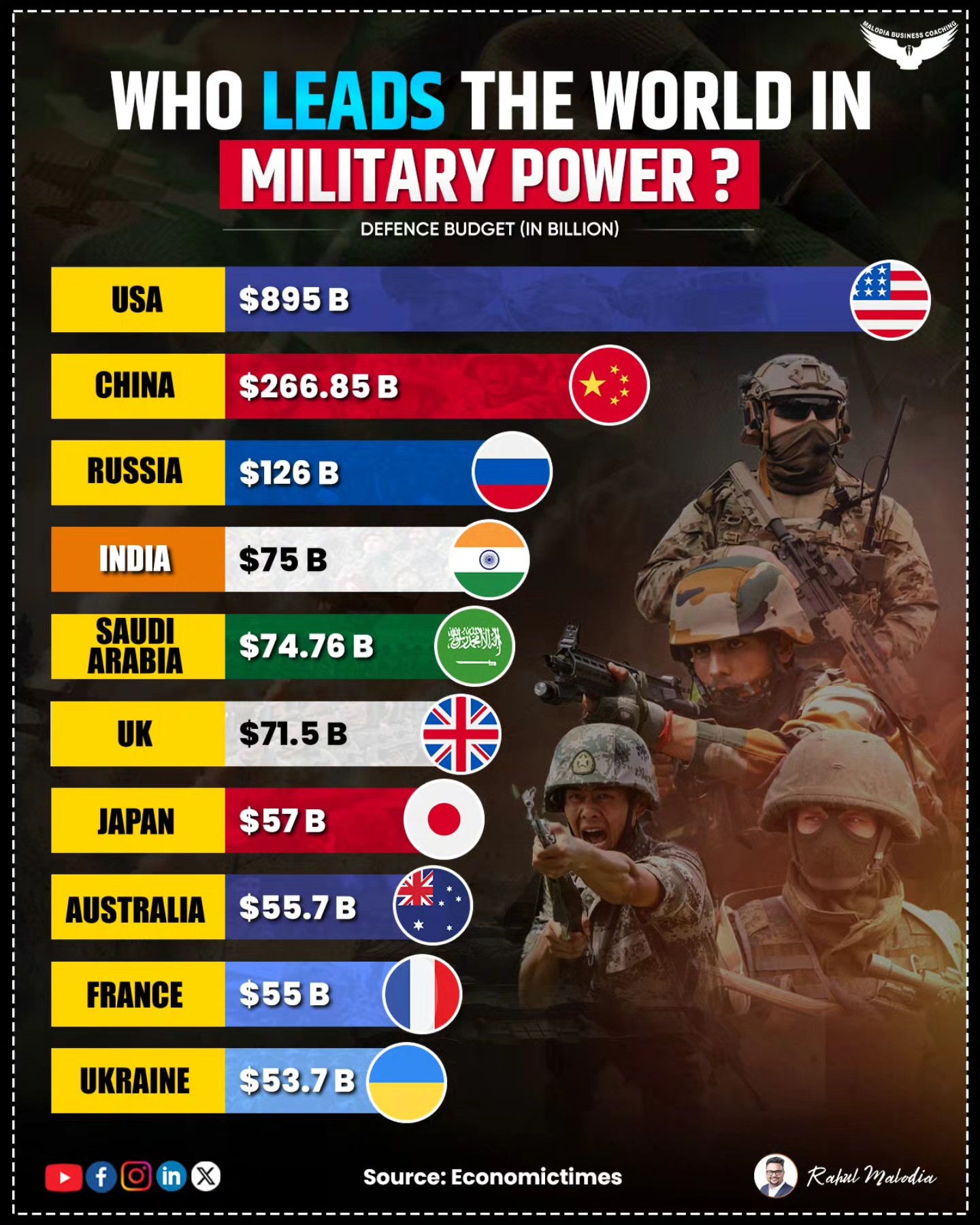
Defence budget (GFP tracked): GFP lists the U.S. defence budget near $895 billion (2025) — the largest worldwide — enabling procurement, R&D and sustainment. (Note: budgets vary by source; GFP maintains a defence-spending list.) Global Firepower
Key strengths: joint operations, strategic lift, C4ISR, precision strike, nuclear triad and robust alliances (NATO, bilateral bases). Global Firepower
Russia (Rank 2)
Why ranked #2: large inventories of tanks, artillery, air defence and one of the largest nuclear arsenals; emphasis on missile systems and layered air defence. Global Firepower
Modernisation highlights: upgrades to air-defence systems (S-500 programme referenced in press), hypersonic missile developments and focus on tactical missile forces. (GFP notes Russia’s strong conventional endowments.) Global Firepower+1
Limitations: sanctions, defence-industry bottlenecks and logistics constraints affect long-term sustainment (widely reported analyses).
China (Rank 3)
Why ranked #3: rapid, continuing modernisation of the PLA — naval expansion (aircraft carriers, submarines), increasing precision-strike and missile units, growth in cyber & space capabilities. Global Firepower+1
Defence spending: China remains the 2nd largest spender (GFP lists ~$245–$267 billion range depending on source/year), funding shipbuilding, aircraft, missiles and R&D. Global Firepower+1
Strategic aim: transition from regional power to limited global maritime power (blue-water navy) and A2/AD capabilities in the Indo-Pacific.
India (Rank 4)
Why ranked #4: large active and reserve manpower, growing numbers of platforms (aircraft, ships, tanks), increasing defence budgets and an expanding indigenous base. Global Firepower
Indigenisation / notable projects:
HAL Tejas Mk1A — Mk1A production/delivery programme to strengthen IAF light combat fleet; contracts and deliveries progressed in 2025. Rediff+1
Arihant-class SSBNs — operational nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine programme (INS Arihant and follow-ons) for sea-based deterrence. Wikipedia+1
BrahMos family — India’s supersonic cruise missile, variants under upgrade (ER / NG / longer range) and maritime & air-launched deployments; export deals (e.g., Philippines) show operationalisation. brahmos.com+1
Defence budget (GFP): GFP lists India among the top five spenders (~$75 billion in 2025), used for procurement, modernisation and indigenisation. Global Firepower
5. Strategic implications (short points useful for GS-3 / Mains)
Great power competition: GFP ranking reflects the conventional balance that shapes strategic competition (US vs China/Russia) and regional security dynamics in Indo-Pacific and Europe. Global Firepower+1
India’s position: As 4th ranked, India has regional deterrence value, but must convert quantity into qualitative readiness, tri-service integration, and sustainment. Global Firepower
Arms modernisation race: rising defence budgets globally (record levels reported in recent years) intensify technology push (hypersonics, AI, cyber, space). The Guardian+1
6. Limitations of GFP (important for critical analysis in answers)
Not scenario-specific: GFP gives a static, comparative snapshot — it does not predict outcomes in specific conflicts or account for alliances. Global Firepower
Qualitative factors under-weighted: morale, leadership, training, doctrine, logistics in wartime, and political will are hard to quantify and may be under-represented.
Nuclear deterrence nuance: nuclear weapons are counted as a factor but GFP is primarily a conventional capability index — strategic deterrence dynamics require separate analysis.
7. How to use this in a UPSC answer (structure + sample pointers)
Intro (1–2 lines): Define GFP and mention 2025 headline (top 4). Global Firepower+1
Body — para 1: Explain GFP methodology (60+ factors; PwrIndx). Global Firepower
Body — para 2: Brief country profiles — US (1), Russia (2), China (3), India (4) — 3–4 bullets each (budget, strengths, notable platforms). Global Firepower+3Global Firepower+3Global Firepower+3
Body — para 3 (analysis): Strategic implications for India & region; mention arms race, technology, logistics. The Guardian+1
Conclusion: Conclude with a balanced sentence on the utility & limits of indices like GFP for policymaking.